Management of underwater munitions
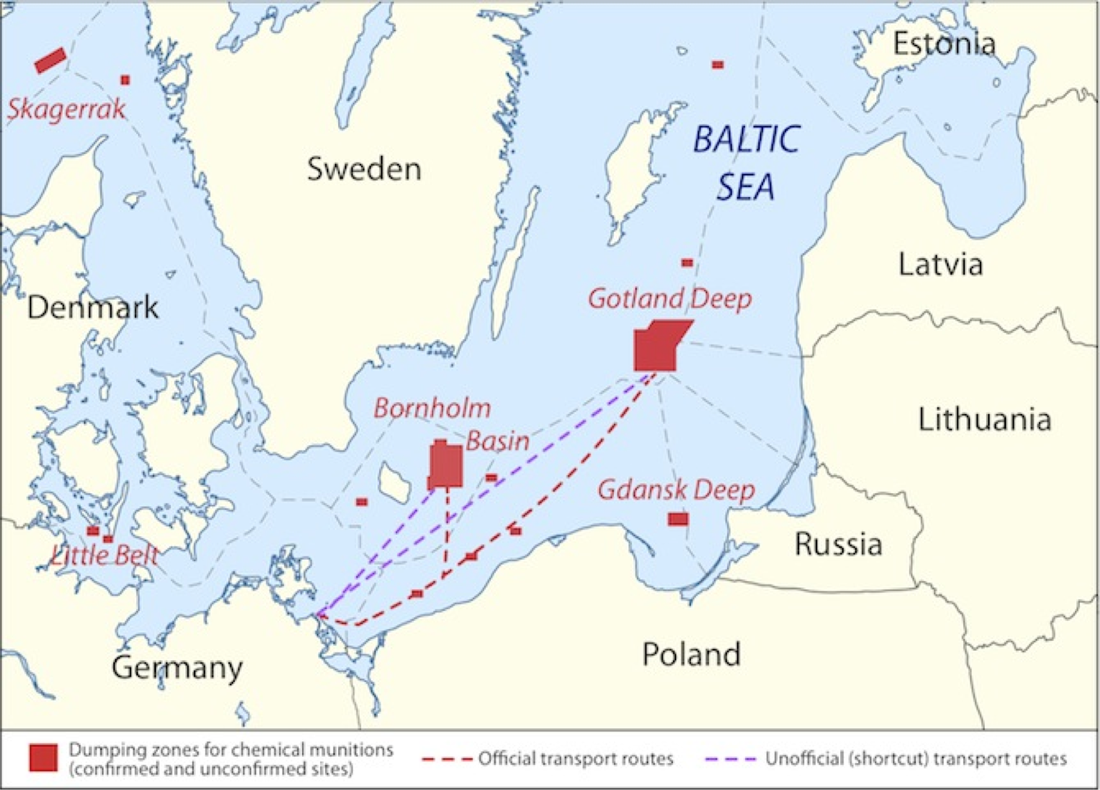
Dumped munitions are a growing concern in the Baltic Sea area. They include chemical munitions dumped after Second World War, and a number of conventional munitions sunk on the sea floor during both world wars. We know, that those munitions are toxic, that they are a hazard for fishermen and offshore activities, but there is no easy solution to this problem. Removing them all would be very costly, while leaving them in place is a potential danger for ecosystem and humans. Some countries and public opinion are requiring action, but how to prioritise the remediation activities? Are they really needed? Will remediation affect the ecosystem? To answer those questions, Decision Aid for Munition Management (DAIMON) programme was formulated.
Developed by the IT specialists from Clausthal University of Technology, the Decision Support System (DSS) uses scientific findings from the DAIMON and related projects about the location, type, condition and ecotoxicologic properties of the documented CWA objects and the surrounding environment.
Developed by the IT specialists from Clausthal University of Technology, the Decision Support System (DSS) uses scientific findings from the DAIMON and related projects about the location, type, condition and ecotoxicologic properties of the documented CWA objects and the surrounding environment.
Decision support sytem The DAIMON DSS involves a databank collecting all project data, survey results, guide lines, cost-benefit analysis, and match-making tool for technical solutions suited for the given area read more
Management optionsDifferent management options for marine munitions have been used globally, but their application to specific challenges encountered in the Baltic Sea has not been evaluated. DAIMON project will review existing procedures and evaluate their suitability for Baltic Sea environmental conditions read more
|
Testing sitesDAIMON's decision support tool was tested in situ on objects detected in pilot areas of the project: in Gulf of Finland and in German coastal waters, Skagerrak strait, Gdańsk Deep and Bornholm Deep and Måseskär read more
|